What is the difference between hybrid inverters and normal inverters?
A normal inverter, such as a traditional solar inverter (PV inverter), primarily functions to convert direct current (DC) from sources like solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use in homes or feeding into the grid. It acts as a simple link between the power source and the electrical system.
In contrast, a
hybrid inverter is a more advanced 2-in-1 solution that combines the functionalities of both a solar inverter and a battery. Beyond converting DC to AC, it can intelligently manage the flow of electricity between solar panels, battery storage systems, and the utility grid. It stores excess solar energy in batteries for later use and can draw power from the grid when needed to charge batteries, optimizing energy usage based on various conditions. This integration eliminates the need for separate inverters, simplifies the system, and enhances energy efficiency by avoiding double conversion losses.
Type of Hybrid Inverter and Work Diagram
Hybrid inverters can be categorized into two main types based on their grid connectivity:
1. Off-grid hybrid inverter: This type does not feed excess electricity into the public grid. It mainly relies on solar panels and energy storage batteries for power supply. When the energy generated by solar panels and stored in batteries is insufficient, it draws supplementary power from the public grid. It is a common choice for areas where grid power is expensive or unreliable.
2. On-grid and off-grid hybrid inverter: This type encompasses all the functions of the off-grid hybrid inverter and adds the capability to transmit excess generated power to the public grid. This allows users to meet their own power needs and sell surplus electricity to the grid, generating additional income.
The working process of a hybrid inverter connected with a solar system and battery storage can be summarized as follows:
1. Solar panels generate DC power.
2. The hybrid inverter converts DC to AC, making it usable for household appliances.
3. Excess AC power (when generation exceeds consumption) is converted back to DC by the inverter and stored in the battery.
4. When solar generation is insufficient or during a power outage, the inverter converts the DC stored in the battery back to AC to supply the household.
5. It can also draw power from the grid to charge the battery or directly power the household when necessary, and feed excess power to the grid (for on-grid models).
The Features and Functions of Hybrid Inverters: What to Look for and What to Avoid
What to look for
1. Power rating: Measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW), it should match the total power consumption of the household, with a margin for safety and future expansion.
2. Surge capacity: The ability to deliver short-term high power to start appliances with high initial demand (e.g., refrigerators, air conditioners), ensuring reliable operation.
3. Efficiency: A high efficiency percentage reduces power losses, maximizing the utilization of solar energy and extending battery life.
4. MPPT voltage range: A wide range allows better adaptation to varying solar panel output conditions, especially in shaded or low-light environments.
5. Battery management: Features like automatic charge/discharge management, full power discharge support, and compatibility with different battery types are important for optimal battery performance and longevity.
6. Monitoring and connectivity: Functions such as remote monitoring, intelligent communication (via RS485, Wi-Fi, 4G, etc.), and 24-hour system monitoring enable users to track energy generation, consumption, and system status conveniently.
7. Protection features: Comprehensive protection against overvoltage, undervoltage, short circuits, overloads, and overheating ensures the safety and durability of the inverter and connected components.
8. Backup power capability: The ability to switch to battery power quickly during grid outages (short backup switch time) is crucial for maintaining power supply to essential loads.
What to avoid
1. Inverters with low efficiency, as they lead to significant energy wastage.
2. Models with limited MPPT voltage range, which may not perform well in diverse weather or installation conditions.
3. Inverters lacking essential protection functions, posing risks to the system and connected devices.
4. Poor compatibility with other system components (solar panels, batteries, grid), which can cause operational issues and reduce system performance.
5. Inverters with no or limited monitoring capabilities, making it difficult to track and optimize system performance.
Is it worth buying a hybrid inverter?
Yes, a hybrid inverter is worth buying for many users, especially those seeking greater energy control and independence. Here are the key benefits:
1. Energy independence: Reduces reliance on the utility grid by storing excess solar energy, allowing use when solar generation is low or during grid outages.
2. Lower energy costs: Increases self-consumption of solar energy, reducing the need to purchase electricity from the grid, especially during peak price periods.
3. Reliable power supply: Provides backup power during grid failures, ensuring essential appliances and devices continue to operate.
4. System simplicity and cost savings: Combines multiple functions in one device, reducing the number of components, lowering installation costs, and saving space compared to separate solar and battery inverters.
5. Flexibility: Can be operated with or without a battery initially, allowing users to add a battery storage system later as their needs and budget permit.
However, it's important to consider the higher initial cost (including batteries) and potential complexity in installation and maintenance. For those with stable grid power, low electricity costs, and no plans for battery storage, a traditional inverter may be sufficient. But for most homeowners and businesses looking to optimize energy usage and enhance resilience, a hybrid inverter offers significant long-term value.
How do you choose a suitable PV inverter?
Choosing a suitable hybrid PV inverter involves considering the following factors:
1. Household power demand: Calculate the total power consumption of your household, including peak loads, to select an inverter with an appropriate power rating and surge capacity.
2. Solar panel system size: Ensure the inverter's input capacity matches the output of your solar panel array, considering the number of panels and their wattage.
3. Battery compatibility: Check if the inverter is compatible with the type and capacity of the battery storage system you plan to use (or may add later).
4. Grid connection needs: Decide whether you need an on-grid/off-grid hybrid inverter or an off-grid model based on your local grid policies and financial goals.
5. Environmental conditions: Consider the installation location (indoor/outdoor) and choose an inverter with suitable protection ratings (e.g., IP65, IP66) to withstand dust, moisture, and temperature variations.
6. Efficiency: Opt for a high-efficiency inverter to minimize energy losses and maximize the utilization of solar energy.
7. Additional features: Evaluate the need for functions like remote monitoring, smart energy management, backup power, and compatibility with other energy sources (e.g., generators).
8. Budget and incentives: Consider the initial cost, including installation, and check for available incentives, subsidies, or rebates for hybrid inverters in your area.
9. Brand reputation and support: Choose a reputable brand with good customer reviews, reliable technical support, and a solid warranty.
The Ideal Hybrid Inverter Brands and Models
AUXSOL
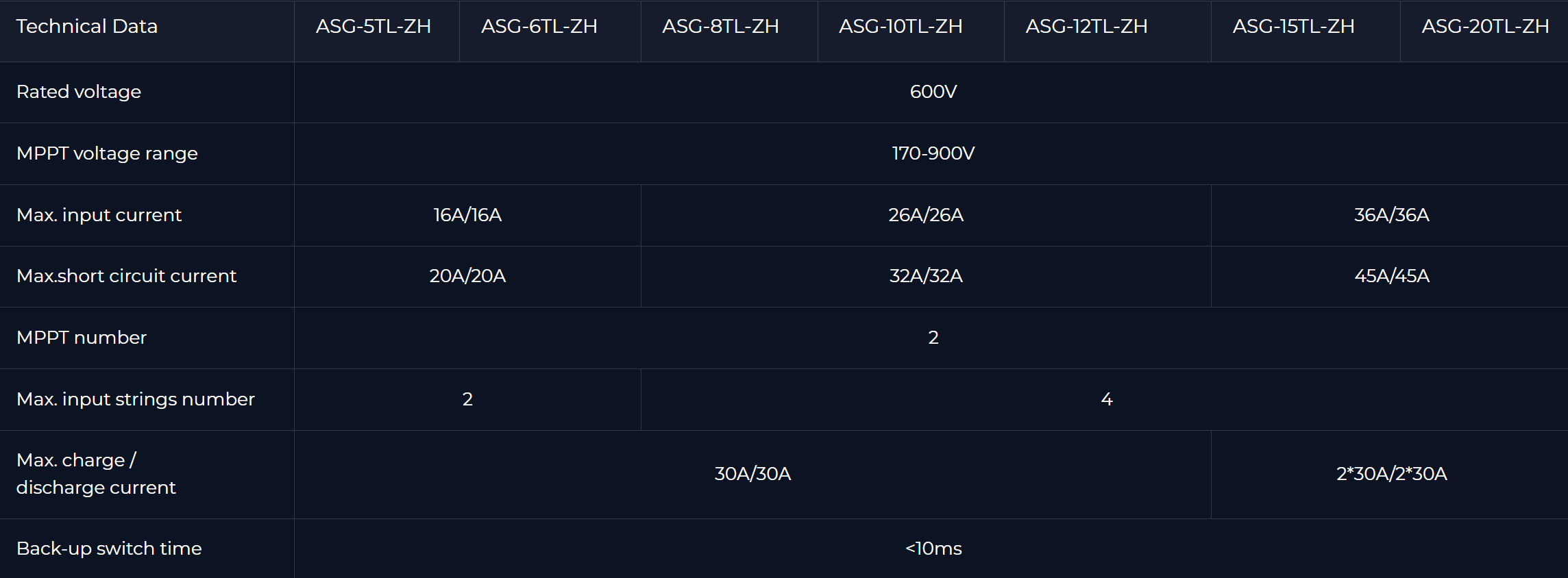
ASG-(5-20)TL-ZH: A three-phase hybrid inverter series suitable for residential installations. It is compact, lightweight, and boasts excellent durability with an ultra-long lifespan. It has an IP66 protection rating, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. Key features include a string current up to 16A, a wide MPPT voltage range, remote diagnosis and updates, 24-hour smart energy management, and easy setup of smart operating modes. Technical specifications include a rated voltage of 600V, 2 MPPTs, max input strings number of 2 or 4, and a back-up switch time of <10ms.