What are PV Systems
Photovoltaic (PV) systems, or solar power systems, convert sunlight into electrical energy via solar cells in panels. These cells generate direct current (DC), which requires conversion to alternating current (AC) for use in homes, businesses, or the grid—making inverters a critical component. PV systems are sustainable, reducing reliance on conventional power and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
What does PV mean on an inverter?
"PV" on an inverter stands for Photovoltaic. A
PV inverter is the core of a solar system, converting DC from PV modules to grid-compliant AC. It also controls and monitors the system, ensuring modules operate at maximum power (adjusting for radiation and temperature) and adhering to safety standards for grid integration.
How many types of PV inverters are there?
PV inverters are categorized by three key traits:
Power output: Ranges from 2 kW (small residential) to megawatts (large power stations). Typical uses: 5 kW (home rooftops), 10–30 kW (commercial), 500–800 kW (utility-scale).
Module wiring (DC design):
1. String inverters: Connect to a single series "string" of modules.
2. Microinverters: Feature short, modular DC wiring directly connecting to 1-2 modules.
3. Central inverters: High-power units with one MPP tracker, suited for large, uniform systems.
Circuit topology:
1. Single-phase vs. three-phase: Single-phase for small systems; three-phase (or multiple single-phase units) for large setups to avoid unbalanced loads.
2. With/without transformers: Transformers provide galvanic isolation (required in some regions) but are bulkier; transformerless models are smaller, lighter, and more efficient.
Which type of inverter is better?
The ideal type depends on system needs:
1. Small systems: Single-phase inverters work well.
2. Large, uniform systems: Central inverters efficiently handle high power.
3. General preference: Transformerless inverters, unless isolation/grounding rules require transformers.
4. Per-panel optimization: Microinverters minimize shading impact on individual panels.
What is the difference between a hybrid inverter and a PV inverter?
A PV inverter converts DC from solar panels to AC for grid use or direct consumption. A hybrid inverter, by contrast, manages energy storage: it converts DC from batteries to AC (for use when solar output is low) and may recharge batteries with excess solar AC, bridging solar generation and storage.
What is the difference between MPPT and PV inverter?
MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) is a function within a PV inverter, not a separate device. It adjusts the inverter’s operation to keep solar panels at optimal power output (dependent on light and temperature). A PV inverter, meanwhile, is the broader device that includes MPPT, converts DC to AC, monitors the grid, and ensures safety—MPPT is just one of its key features.
How long does a PV inverter last?
PV inverters typically last 10–15 years, shorter than solar panels (25–30 years with <0.4% annual degradation). They may need replacement once during a panel’s lifespan, making durability and warranty terms important considerations.
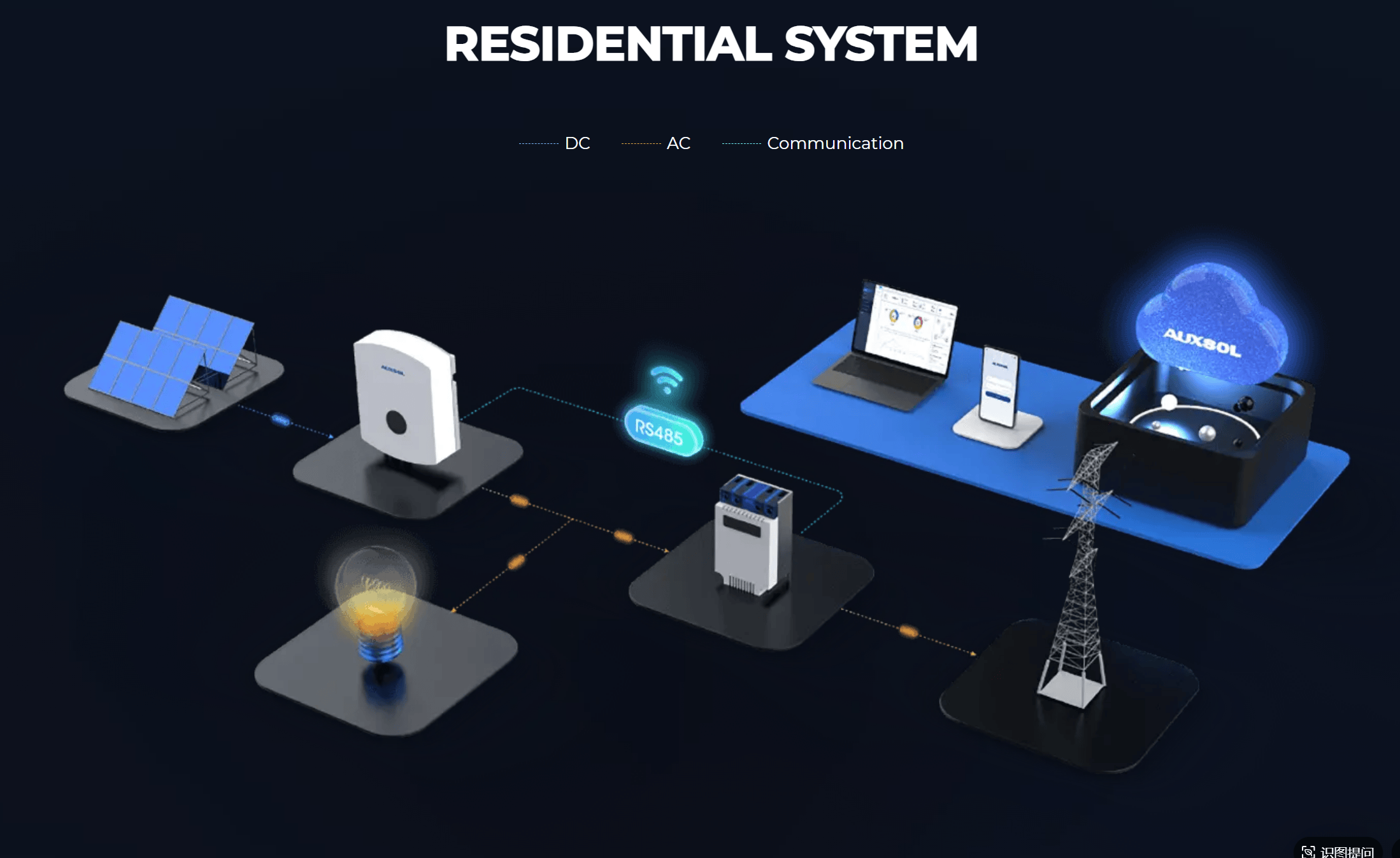
Residential Solar Inverter Solutions from AUXSOL
AUXSOL’s
residential systems include on-grid inverters, hybrid inverters, batteries, and off-grid inverters, with 3.6–25kW inverters adaptable to various rooftops. Their on-grid inverter models (e.g., 5–25kW three-phase
ASN-(5-25)TL, 7–10kW single-phase
ASN-(7-10)SL) feature 2 MPPT trackers and support 4G/WIFI/RS485 communication with the AUXSOL cloud platform for remote monitoring.
Key considerations when selecting an Inverter
1. Power matching: PV array capacity should exceed the inverter’s by ≤10% to avoid underperformance during high radiation.
2. Voltage compatibility: Ensure maximum DC voltage from panels does not exceed the inverter’s input limit.
3. Efficiency: Prioritize high conversion rates (modern models reach ~98%).
4. Durability: IP65-rated enclosures allow outdoor installation; efficient cooling sustains performance at up to 50°C.
5. Communication: Interfaces like 4G/WIFI/RS485 enable monitoring via platforms (e.g., AUXSOL cloud).
6. Warranty and reliability: Choose trusted brands with strong warranties to ensure long-term performance.